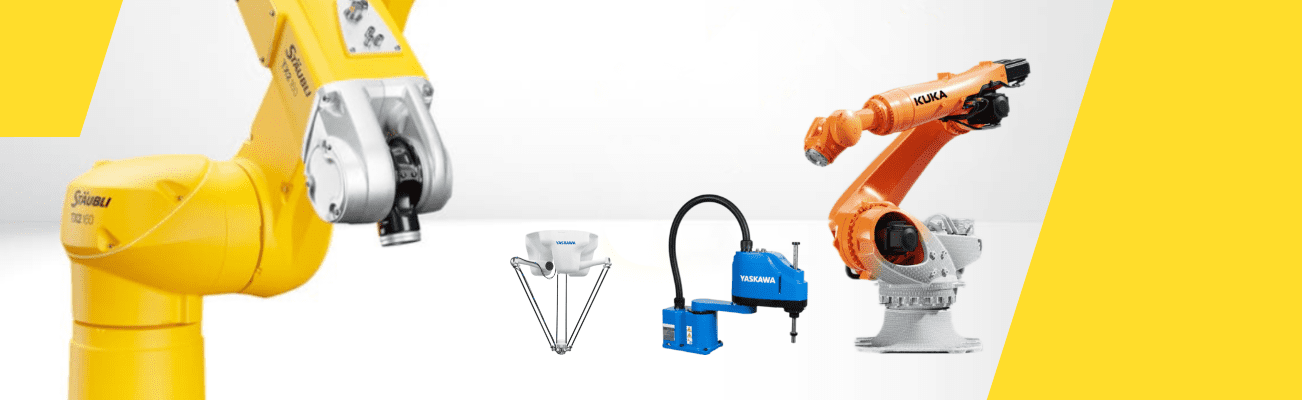
Industrial robots weld, mill, fold, paint, pack - they help workers perform monotonous and heavy tasks in automatic mode. Modern enterprises use linear, articulated, delta and scara robots. The task for automation determines which robot to use. Initially the task determines the type of robot, and then the robot is selected according to the parameters of the required load capacity and operating range. This article will help you figure out what types of robots there are and for what tasks they are used.
What types of industrial robots are there?
Industrial robots are divided by design and connection of axis - there are 6 types.
1. Cartesian robot (linear robot)
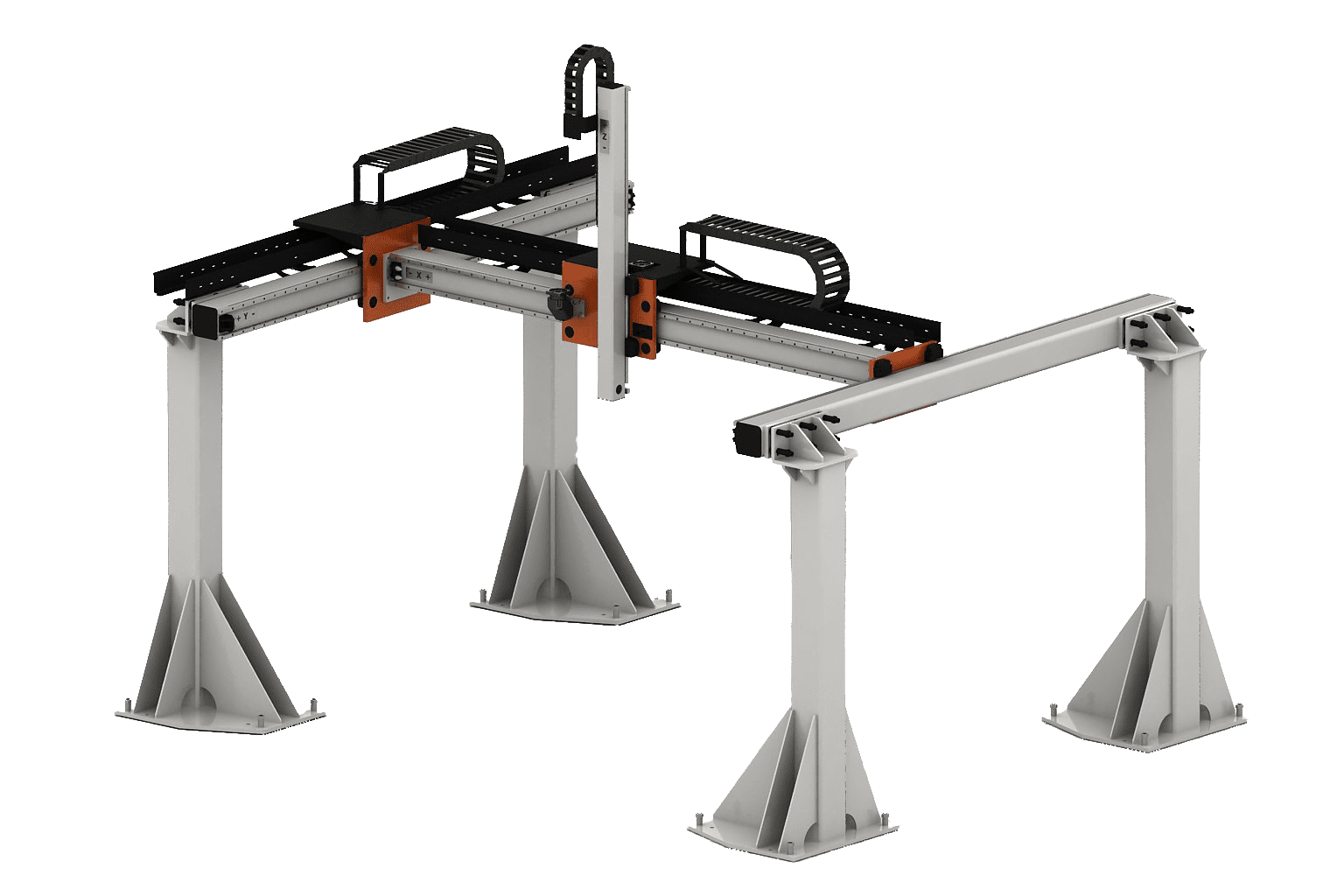
The Cartesian robot is similar in design to a bridge crane with three axes of movement, has a high load capacity and accuracy. In a Cartesian robot, the axes are perpendicular to each other and the robot moves along them in a straight line, hence the second name linear. Such robots are used to move material, load and unload machines, palletize, weld and assemble products.
Advantages:
- The Cartesian robot is programmed along only three axes and it is considered easy to operate;
- Positioning accuracy of linear robots can reach up to 0.1 mm;
- The Cartesian robot is capable of moving heavy loads at distances of over 4 meters;
Disadvantages:
- Linear robots are bulky and require a lot of space for installation;
- The robot's open mechanisms are susceptible to dirt contamination resulting in high wear of parts.
2. Cylindrical robot
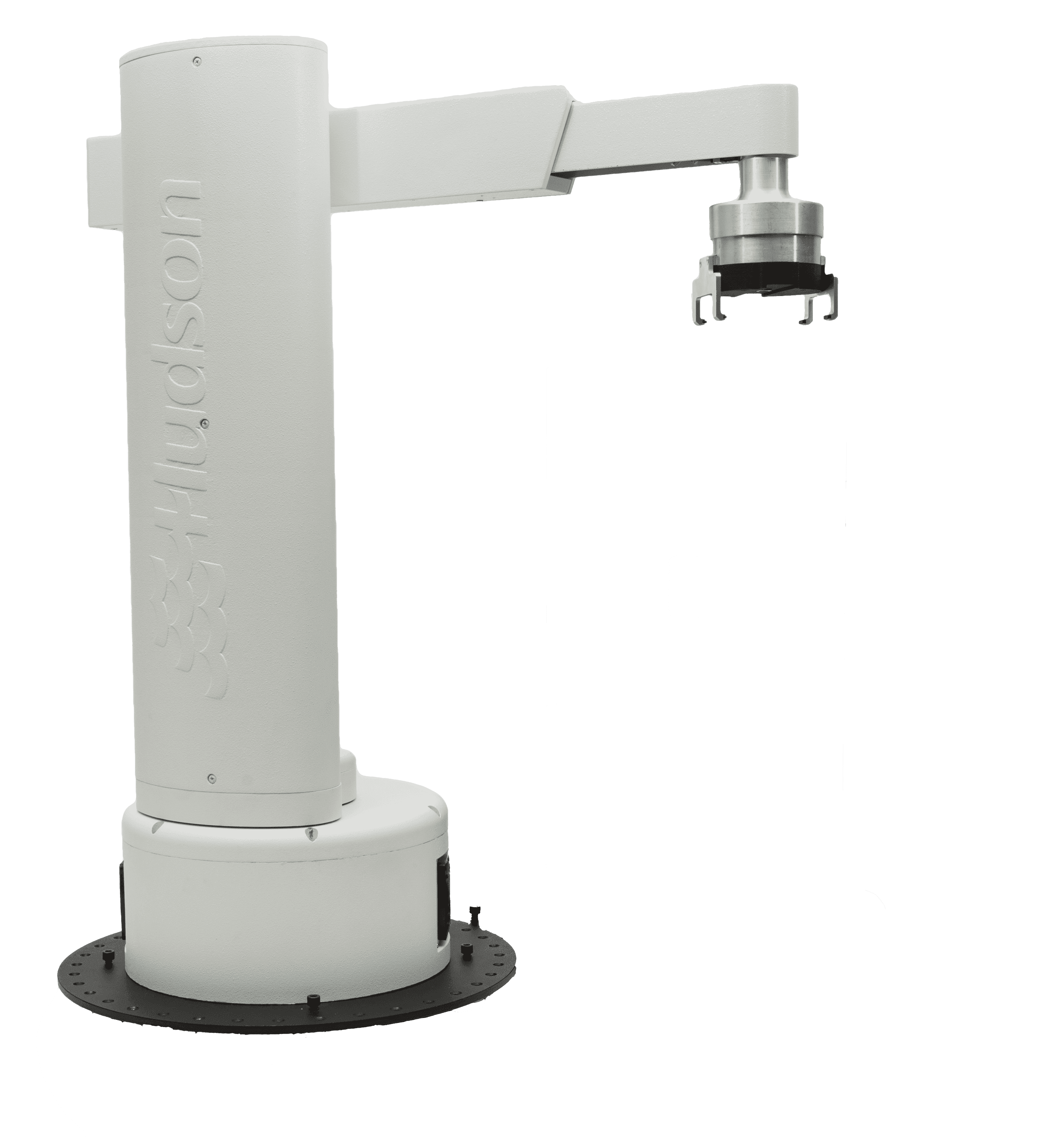
A cylindrical robot is a three-axis industrial robot with a working area in the shape of a cylinder, two axes of the robot have a linear stroke, and the third is circular. This type of robots is used for pipe welding, spot welding, machining, machine tool maintenance and material transfer.
Advantages:
- Requires little space for installation;
- The cylindrical robot can perform operations in hard-to-reach areas - channels and hollows within its spherical working area;
Disadvantages:
- Low accuracy and repeatability;
- Limited working area;
- The robot is limited in the ways it can manipulate objects, it can move them from one plane to another, however it cannot rotate them.
3. Spherical robot
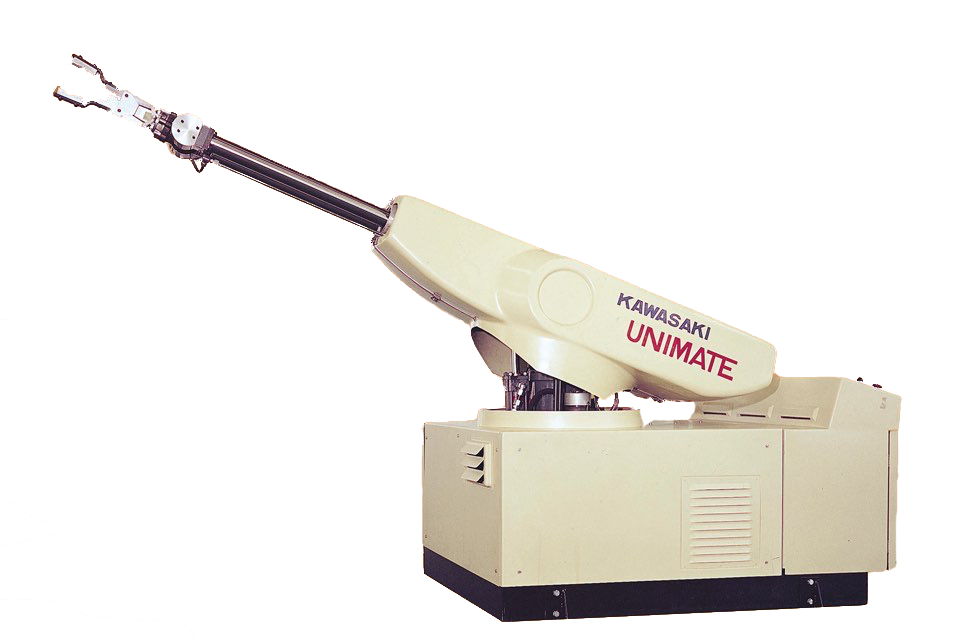

A spherical robot or a robot with a polar coordinate system is the first industrial robot that was used for welding, moving parts, machining and loading machines. Spherical robots have two axes of rotation and one linear axis, making a spherical working area, within which the robot is able to reach any point.
Advantages:
-
Long reach;
Disadvantages:
-
Low accuracy and repeatability.
4. SCARA robot
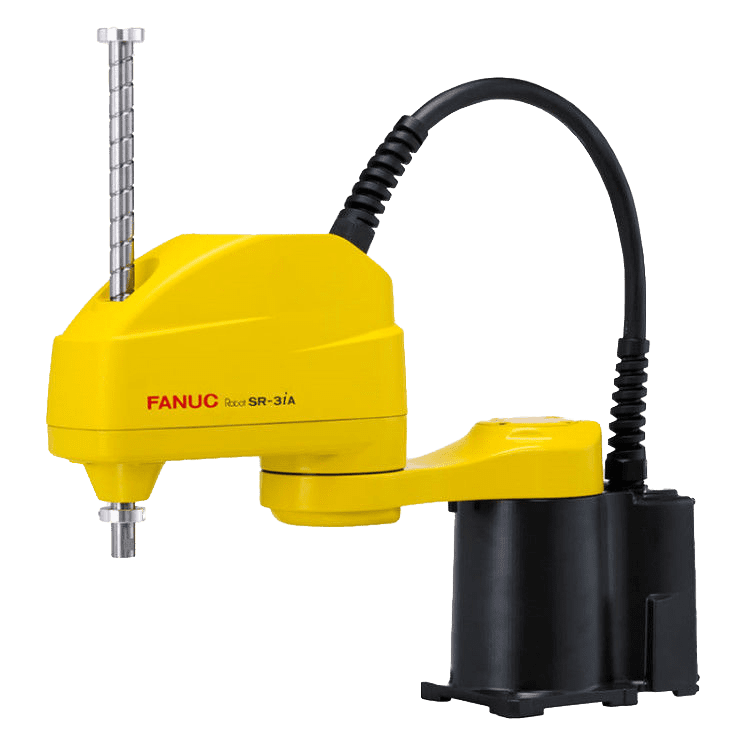

SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) are high-precision and high-speed industrial robots with four axes of motion. The robot's joints move in a horizontal plane along three axes, and the tool moves linearly up and down along the fourth axis. SCARA robots are used on high-speed production lines for assembly, material movement and packaging.
Advantages:
-
High speed and accuracy;
-
Compact dimensions;
Disadvantages:
-
Limited working area;
-
Low load capacity
-
The robot cannot twist and flip an object
5. Articulated robot
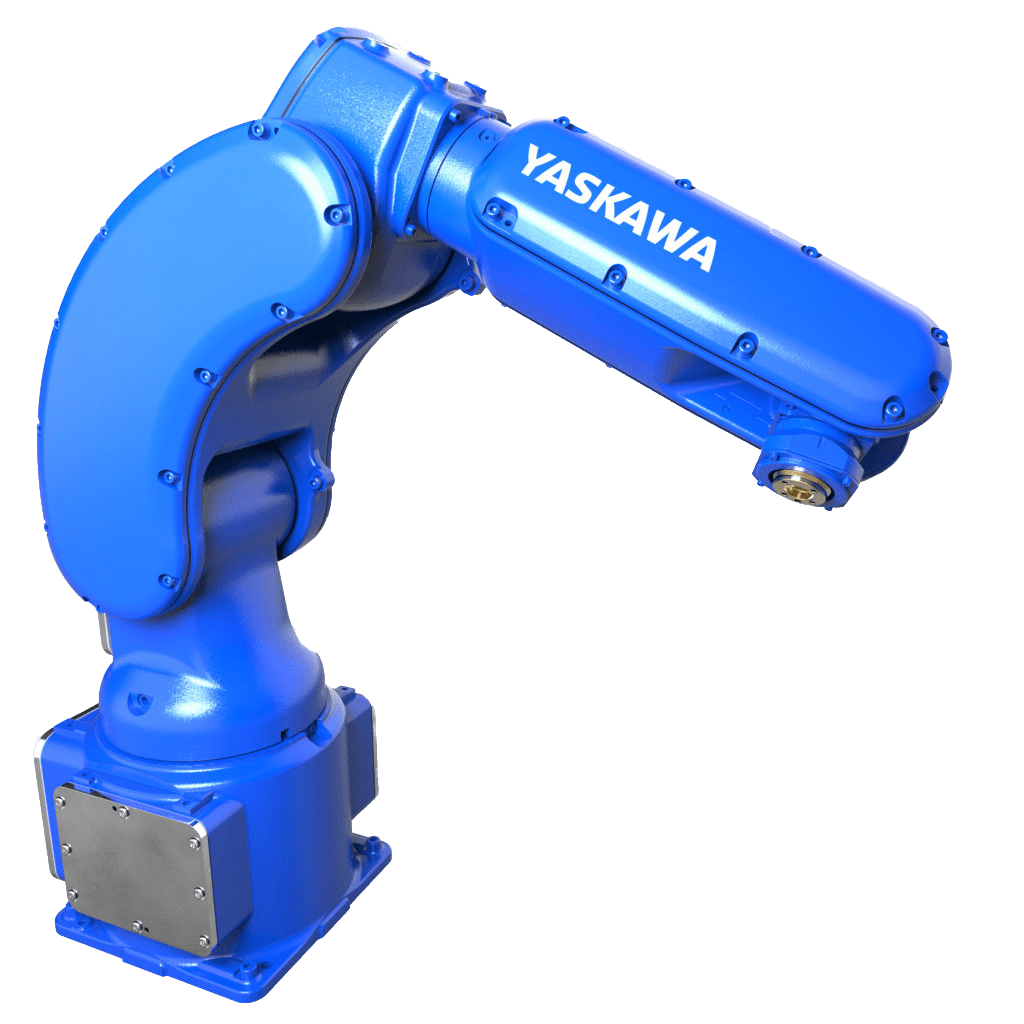

Articulated robots are six-axis industrial robots consisting of sequentially connected joints, mimicking the design of a human hand. Six axes of mobility give articulated robots flexibility and allow them to reach hard-to-reach points that other types of robots will not be able to reach. Articulated robots are the most common type robots and are used for most repetitive tasks from welding to painting.
Advantages:
-
Versatile and flexible - one model can be used for completely different tasks;
-
A large selection of various parameters;
-
Applicable in various specific conditions - food production, clean rooms, low and high temperatures;
-
Can be placed in a limited space with various mounting options - floor, wall, ceiling;
Disadvantages:
-
Complex programming.
6. Delta Robot
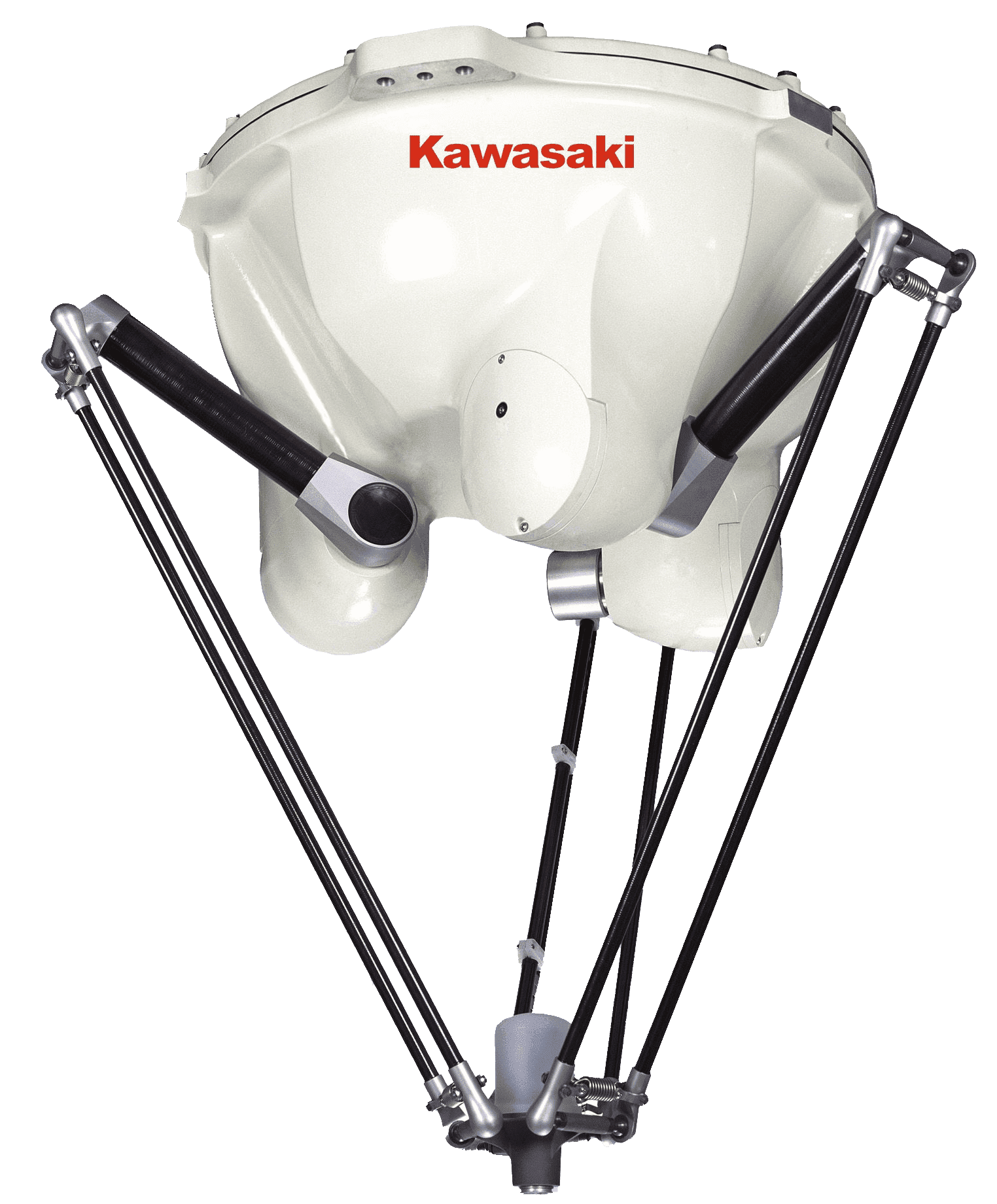
Delta robot aka parallel robot and spider robot is an industrial robot consisting of three levers attached to the base and holding the robot tool parallel to the base. Delta robots come 3, 4 and 6 axis variants. 3-axis delta robots can move an object from one plane to another parallel to the first, and robots with a large number of axes are able to flip objects and grab them from different sides. Delta robots are used on high-speed production lines for packaging, assembly and sorting.
Advantages:
- High speed and accuracy;
- Takes up little space;
Disadvantages:
- Limited working area;
- Low load capacity.
Each type of industrial robots has its advantages and is good at certain types of tasks. Although the articulated robot is a universal solution for most tasks, in your particular situation it may be more appropriate to integrate a linear robot or a SCARA. It is better to entrust this task of choosing an appropriate robot to the integrator. Leave a request and we will find you an industrial robot that suits your needs and help you solve the problems of your production.
![[Alt]](/images/logo-min.png)



